Monday, October 26, 2009
Lec 10 : Cyberlaws
Cyberlaw is important because it touches almost all aspects of transactions and activities on and concerning the Internet, the World Wide Web and Cyberspace. Initially it may seem that Cyberlaws is a very technical field and that it does not have any bearing to most activities in Cyberspace. But the actual truth is that nothing could be further than the truth. Whether we realize it or not, every action and every reaction in Cyberspace has some legal and Cyber legal perspectives
Tuesday, October 20, 2009
Lec 9 : Legal and Ethical Issues in Computer Security
On the other hand, ethics has not bad to change, because ethics is more situational and personal than the law. And although technically this issue is just an aspect of confidentiality, practically it has log history in both law and ethics. This chapter too discuss is round out study of protection for computing system by understanding the context in which security is assessed and applied. Not always are conflict resolved pleasantly. Some people will think that they have been treated unfairly, and some people do indeed act unfairly.
Law and computer security are related in several ways. First, international, federal,state,and city laws can affect privacy and secrecy. These statues often apply ti the rights of individuals to keep personal mattes private. Second, laws regulate the use, development and ownership of data and programs. Patents, copyrights and trade secrets are legal devices to protect the rights of developers and owners of programs and data. Similarly, one aspect of computer security id controlling access to programs and data that access control is support by the mechanisms.
Thursday, October 15, 2009
Lec 8: Wireless Security
- Disable the services set identifier (SSID) broadcast
- MAC addressing filtering
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) authentication
- WEP data encryption
Security in 802.11 was found to be seriously flawed in several areas 802.11 was developed to correct the shortcomings of security in 802.11. The WiFi also improved security for wireless networks with WiFi protected Access (WPA, WPA2) for home network use, called personal, and for business network use, called Enterprise. WPA uses an acceptable encryption algorithm that is strong and easier on the devices performing the encryption. WPA2 uses a significantly stronger algorithm that is considered uncrackable, but the performence of devices may suffer with the heavy work load.
Thursday, October 1, 2009
Lab 7 : Security in Application
As a user,can use FTP with a simple command line interface (for example, from the Windows MS-DOS Prompt window) or with a commercial program that offers a graphical user interface. Your Web browser can also make FTP requests to download programs you select from a Web page. Using FTP, you can also update (delete, rename, move, and copy) files at a server. You need to logon to an FTP server. However, publicly available files are easily accessed using anonymous FTP.
Basic FTP support is usually provided as part of a suite of programs that come with TCP/IP. However, any FTP client program with a graphical user interface usually
Tuesday, September 29, 2009
Lec 7 : Security Application
world is become expand especially in term of technology. For example, biometric technology and fingerprint recognition. At the same time, it also came with
advantage and disadvantage.
Wednesday, September 23, 2009
lab 6 Database security
Lec 6: Security In Network
It's important to build systems and networks in such a way that the user is not constantly reminded of the security system around him. Users who find security policies and systems too restrictive will find ways around them. It's important to get their feedback to understand what can be improved, and it's important to let them know why what's been done has been, the sorts of risks that are deemed unacceptable, and what has been done to minimize the organization's exposure to them.
Monday, September 21, 2009
Lec 5 : Database Security
Traditionally databases have been protected from external connections by firewalls or routers on the network perimeter with the database environment existing on the internal network opposed to being located within a demilitarized zone. Additional network security devices that detect and alert on malicious database protocol traffic include network intrusion detection systems along with host-based intrusion detection systems.
Database security is more critical as networks have become more open.
Databases provide many layers and types of information security, typically specified in the data dictionary, including:
* Access control
* Auditing
* Authentication
* Encryption
* Integrity controls
Database security can begin with the process of creation and publishing of appropriate security standards for the database environment. The standards may include specific controls for the various relevant database platforms; a set of best practices that cross over the platforms; and linkages of the standards to higher level polices and governmental regulations.
Monday, September 7, 2009
Lab 5 Web Application Security
2. Web Application Hacking simulation using WebGoat and WebScarab, if u want download this sofware, click the link above :
http://www.owasp.org/index.php/Category:OWASP_WebGoat_Project http://www.owasp.org/index.php/Category:OWASP_WebScarab_Project
Command Prompt opens and vanishes instantly, and another Command Prompt window opens titled "Tomcat". The Tomcat window fills with text and stays open, as shown below. This is the Apache Tomcat Web server listening on the localhost, port 80.
Sunday, August 16, 2009
Lab 4 : Cryptography Extended
A cipher or cryptosystem is a method for message concealment.
The key provides the means for efficient encipherment (encryption).
Plaintext – message in readable form
Ciphertext – encrypted message

message.
- one key for encipherment
- A second key for decipherment
EACH column of this table forms a dictionary of symbols representing thealphabet: thus, in the A column, the symbol is the same as the letterrepresented; in the B column, A is represented by B, B by C, and so on.
Friday, August 14, 2009
Lec 4: Operating System Security
second, we identify that the today commercial operating system use protection systems that fail so truly enforce security goals. we defined a mandatory protection system which will enforce security in the face of attack
third, we outline the architecture of an access enforcement mechanism that would be implemented by a protection system. Such enforcement mechanisms can enforce a mandatory protection state correctly if they satisfy the guarantee required of the reference monitoring concept
Finally, we defined requirements for a secure operating system based on a reference monitor and mandatory protection style.
Monday, August 10, 2009
Lab 3: Authentication and Basic Cryptography
a. Open Windows Explorer or My Computer.
b. Right-click the file or folder that you'd like to encrypt or unencrypt and select Properties.
c. On the General tab, click the Advanced button.
d. From the Advanced Attributes dialog box, mark (or clear) the Encrypt Contents to Secure Data check box to encrypt (or unencrypt) the file or folder that you selected. Click OK to close the Advanced Attributes dialog box and then click OK for the properties sheet to apply this setting. (When you encrypt a folder, you are prompted to select between applying this setting to the folder only and applying it to the folder, subfolders, and files.)
e. To share access to an encrypted file, click the Details button from the Advanced Attributes dialog box. You cannot share access to encrypted folders.
f. From the Encryption Details dialog box, click the Add button to add more users' EFS certificates to the encrypted file to share access with those users.
g. From the Select User dialog box, click the user whose EFS certificate you want to add for shared access to the encrypted file and click OK. You see only certificates for users who have encrypted a folder or file previously.
h. Click OK for the Encryption Details dialog box.
i. Finally, click OK for the Advanced Attributes dialog box and then click OK for the Properties window
Account Lockout Policy
You can access Group Policy settings by opening the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) and adding the Group Policy snap-in.
The Acount Lockout Policy controls settings related to users attempting to login and entering wrong passwords. While it is possible to set this up so that a person can sit there and try thousands of different passwords in an attempt to find the right one, this is highly unwise and a serious compromise of security. There are three settings for this policy and using them will greatly increase security.
Access the Account Lockout Policy from:
Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Account Policy -> Account Lockout Policy
The Password Policy controls settings related to each user's passwords. It is important to enforce a password policy, because the chances of a user giving out their password (accidently or intentionally) is very high. Thus, requiring them to change their password reasonably often and have it conform to a set of standards that make it very difficult to crack is in your organization's best interests.
Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Account Policies -> Password Policy
Sunday, August 9, 2009
Lec 3: Program Security
The total amount of damage already done is not measurable, but it is certainly large. Many successful attacks go undetected—for now, at least. With the explosive growth in connectivity to massive public networks such as the Internet, the exposure to threats is increasing dramatically. Yet the public continues to increase its reliance on computers and networks, ignoring the obvious danger.
In this chapter, we considered two general classes of security flaws: those that compromise or change data and those that affect computer service. There are essentially three controls on such activities: development controls, operating system controls, and administrative controls. Development controls limit software development activities, making it harder for a developer to create malicious programs. These same controls are effective against inadvertent mistakes made by developers. The operating system provides some degree of control by limiting access to computing system objects.
Finally, administrative controls limit the kinds of actions people can take. These controls are important for more than simply the actions they prohibit. They have significant positive effects that contribute to the overall quality of a system, from the points of view of developer, maintainer, and user. Program controls help produce better software. Operating systems limit access as a way of promoting the safe sharing of information among programs. And administrative controls and standards improve system usability, reusability, and maintainability.
For all of them, the security features are a secondary but important aspect of the controls' goals. Program controls are part of the more general problem of limiting the effect of one user on another. In the next chapter, we consider the role of the operating system in regulating user interaction
Saturday, July 25, 2009
Lab 2: The Goals of Information Technology
Step 1 : Click on the Start button, then select the "Run" command. This will open a small box with a text field. In this field, type 'cmd' without the quotes and press enter.
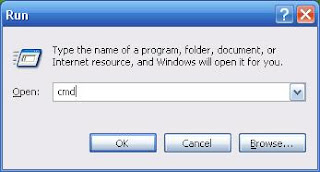
Step 2 : At the resulting prompt, type in: chkntfs /d: [Enter]
If the message show “D: is not dirty”. This means that there is no corruption on the drive.

Step 3 : Now that we're in the command console, you'll need to enter in the command that will convert the drives. Make sure you type in the command exactly as it's shown (replace 'X:' with the drive letter you need to convert: CONVERT X: /FS:NTFS [Enter]

Step 4 : Close all Windows and log off
Data Confidentiality.
Use NTFS permissions to specify which users and groups can gain access to files and folders, and what they can do with the contents of the file or folder. NTFS permissions are only available on NTFS volumes. The permissions you assign for folders are different from the permissions you assign for files.
You assign folder permissions to control the access that users have to folders and to the files and subfolders that are contained within the folder.
Step 1 : Select Start >>Programs>>Administrative Tools >> Computer Managment
Step 2 : Choose >>Local User and Groups and double clickon the "user" folder.
Step 3 : Create the New User account by selecting User>>New User. The New User dialog box appears.
Step 4 : Complete these fields in the New User dialog box:
a. In the Username field, enter OpenView.
b. In the Full Name field, enter OpenView Administration.
c. In the Description field, enter Permit operation from OpenView services.
d. In the Password field, enter your password.
e. In the Confirm Password field, re-enter your password
f. Click button [Create]
_______________________________________________________________________
Creating data Confidentiality between 2 user accounts.
Step 1 : Log on to the Windows 2003 server as Administrator.
Step 2 : Create a new folder called Confidentiality.
Step 3 : In F0lder Confidentiality, crate another new folder called User1Folder
Step 4 : Right-click User1Folder >>[Properties] >> open the User1Folder Properties
Step 5 :Right-click the file or folder for which you want to assign permissions, In the Security tab
Step 6: Click on the Advanced Button
Step 7 : To add permissions to user accounts or groups for the folder, click Add
Step 9 : Uncheck the box “Allow inheritable permissions from parent to propagate to this object”.
Step 10 : Click [Copy] to retain the permissions.
Step 11 : Click [Add] and the Select Users, Computers, or Groups.Step
Step 12 :Type User1 and then click [Checks Names] and click OK
Step 13 : click the Allow Full Control box and then click OK for Permission Entry windows, .
Step 14: Remove the other username except Administrator, System and User1 by clicking the username
Step 15 : Click OK and Double-click User1Folder and you should see the content of the folder
Step 16 : All windows and log off close
Step 17 : Log on as User2 and navigate to the User1Folder, try to open this folder
Step 18 : Close all windows and log off.
Special permissions are set on the Permission Entry For dialog box for the file or folder. This dialog box is accessed by selecting Advanced on the Security tab of the Properties dialog box for the file or folder, and then selecting View/Edit for a Permission Entry on the Access Control Setting For dialog box for the file or folder.
Friday, July 24, 2009
Lec 2: Authentication & Basic Cryptography
assurances that the identity of another (the claimant) is as declared, thereby preventing impersonation. The most common technique is by the verifier checking the correctness of a message (possibly in response to an earlier message) which demonstrates that the claimant is in possession of a secret associated by design with the genuine party. Techniques which provide both entity authentication and key establishment are often integrated, Other names: entity authentication, identity verification
Cryptography to increase privacy:
There are two basic methods for data encryption:
- Symmetric key cryptographydata is encrypted and decrypted with the same key. the strength of encryption depends on the size of the key: a key with less than 40 bits is to be considered insecure, while a key with more than 128 bits is fairly unbreakable.the problem is: how get both parties the secret key in the first place
-Public key cryptographypublic key cryptography requires two keys, a secret ("private") key and a well known ("public") key. there are two different scenarios where public key cryptography may be used:
1. Send a secret message that only a particular receiver shall be able to read:the sender encrypt the message with the receiver's public key, only the holder of the corresponding private key can decrypt an read the message.
2. Digital signatures:the author of a document encrypts the text with his private key. anyone who knows the authors public key can decrypt and read the message, this reliably authenticates the author.
Saturday, July 18, 2009
Lab 1: Introduction to Virtualization & VMware
WHAT IS VIRTUAL MACHINE?
A virtual machine (VM) is an environment usually a program or operting system, which does not physically exist but is created within another environment. In this context, a VM is called a "guest" while the environment it runs within is called a "host" while the environment it runs within is called a "host." Virtual machines are often created to execute an instruction set different than that of the host environment
VMware Workstation Installation.
VMware Workstation Can be Downloaded from http://www.vmware.com/download/ws/
1. Double Click on the VMware launcher to start the installation Wizards
2. Click on [Next].
3. Choose Typical setup type
4. Choose the location for VMware Workstation installation, example: C:\Program
Files\WMware\VMware Workstation\, Click on [Next]. 
5. Configure the shortcuts for the VMware Workstation and click [Next].
6. Click on [Install], this will take several minutes to finish

7. Enter the Serial Number for the VMware workstation.

8. Click [Finish], and restart the Computer.

VMware
VMware Workstation makes it possible for PC user to use Multiple Operating Systems. Concurrently on the Same PC. User can create and run multiple virtual machine on desktop or laptop computer. VMware Workstation let you create a virtual machine that can be installed with different kinds of Operating System. Each virtual machine virtualized a complete set of PC, including Memory, HDD, network connections, peripheral ports and processor.

Creating Disk Image
1. From the home tab click on [New Virtual Machine], to open the virtual machine wizard

2. Click [Next] to continue.
3. Choose the typical configuration, click [Next]
4. Choose the type of OS to be installed on the virtual machine. As the next task the virtual machine will be installed with Windows Server 2003, select [Microsoft Windows] as the guest. In the version list, select Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition. Click [Next]. Refer figure 1.10.

5. Name the virtual machine and specify the location where the disk image for the virtual machine
will be stored in the hard disk. Name the virtual machine as winserv03.

6. For the network type select [Use host-only Networking], this selection will create LAN between the other virtual machine.In order to make the virtual machine connected to the real network select [Use bridged networking]. This setting can be changed once the virtual machine is created. Click[Next]. Refer figure 1.12.

7. Specify the disk capacity of the virtual machine. This option will let user to specify the maximum storage capacity of the virtual machine. In this task set the storage capacity between 2GB to 4GB (Depends on the size of your PC). Select [Allocate disk space now] and click [Finish] to start creating your virtual

8. Once your disk image that holds you virtual machine is created you will see figure 1.14. Click [Close]

Get to know the virtual machine console.
Once the virtual machine is created, the tab will contain the home and summary view of winserv03 virtual machine configuration. Refer figure1.15
.

3. Once the winserv03 booting you will see the familiar windows server 2003 installatio page from this point onward you can follow the windows server 2003 installation step.
4. After the installation process is finish, you will see the windows server 2003 login page.
Lec 1: Introduction to information security
First we must know the meaning of IT security? The concept of IT security is of quality or state of being secure that is to be free from danger and to be protected from adversaries from those who would do harm, intentionally or otherwise. Besides, we must know the the type of security area, the type of security area is security architecture, security principles, security policy, and security attacks/ threats.
Example of Active Attacks




Example Of Passive Attacks





















